For years, I’ve been talking shit about broad match keywords.
My advice has been simple: stay away from this keyword match type, especially if you are new to Google Ads.
That’s because in all the accounts I’ve audited, broad match keywords are one of the key reasons for a poor ROI.
So in this article, I want to show you the details of what happens in you (accidentally) use a broad match keyword in one of your campaigns.
Let’s dig in!
Table of Contents
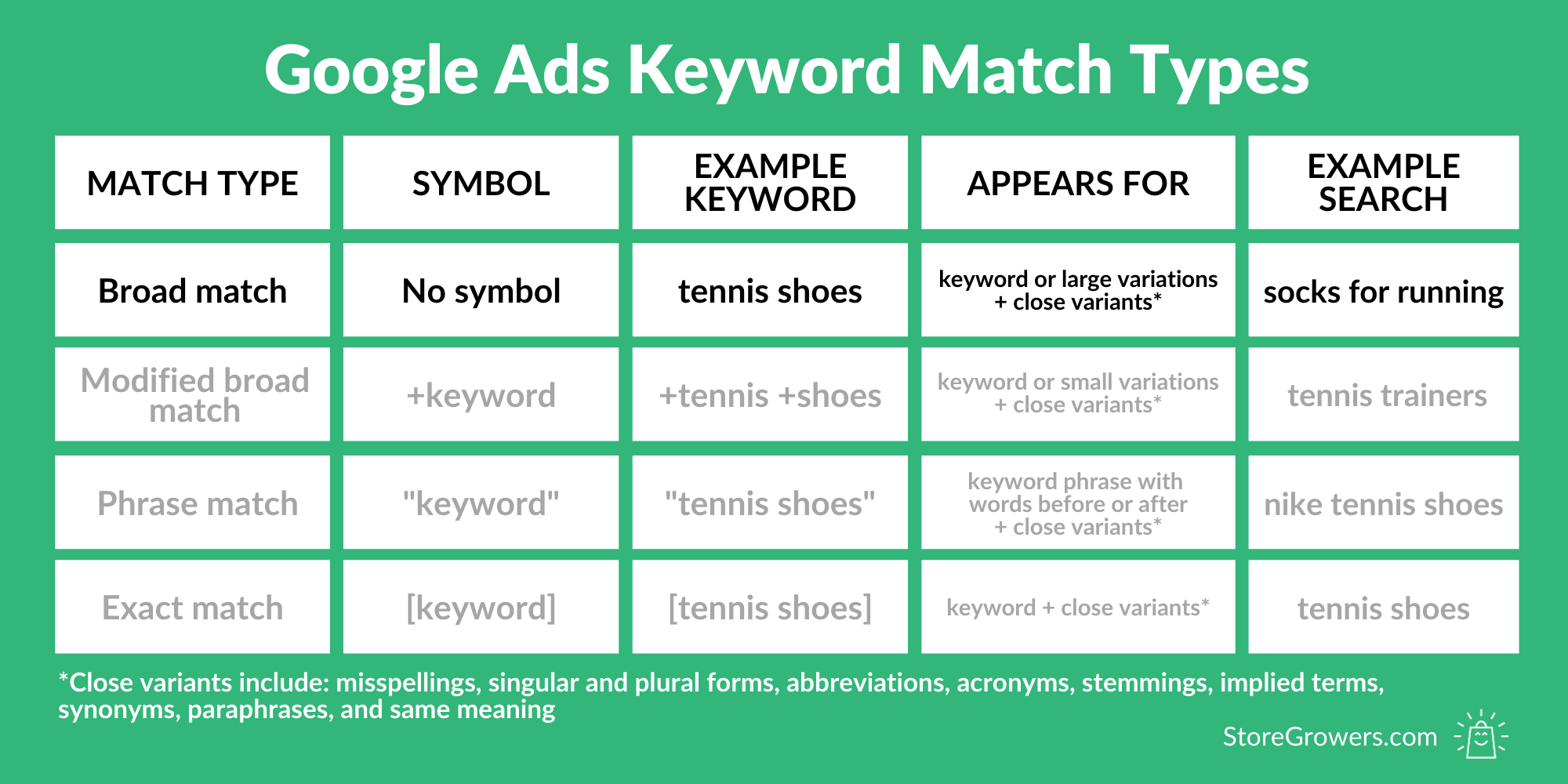
What is Broad Match?
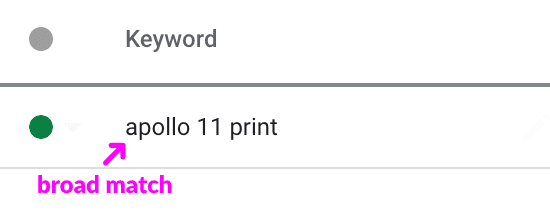
Here is how Google defines broad match:
A keyword option that allows your ad to show when someone searches for that keyword, variations of it, as well as other related topics.
To me, here is what broad match means:
It is the default match type and by using it you give Google total control over which search queries your ads show up for.
Since its the least restrictive of the four available match types, your ads will show for search queries that you aren’t really expecting.
Here are two examples from the Google support docs:
| broad match keyword | Show up for |
| bicycle bell | cycling accessories blue bicycle helmets bell reviews for bikes |
| hats | hat sun hats winter accessories sombreros |
Since Google is pretty straightforward about how random the matched search queries can be, you might wonder what the problem is.
The Problem with Broad Match
The big problem with broad match is that it is not the best option for people starting out.
It’s an unkown unknown. New advertisers don’t have a clue about match types let alone that what broad match is.
Here is the place where you select your keyword match type:
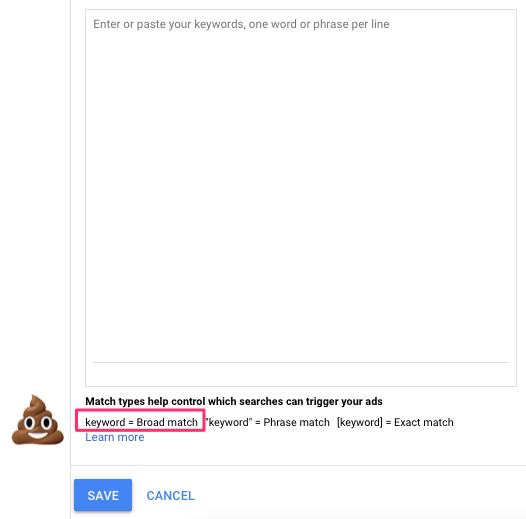
A big box to put in keywords, and a small snippet of text below the box with some match type instructions.
But it doesn’t matter much if you tell them the keywords are broad match if they don’t understand what it is right?
That’s not a fault of the user, this is 100% Google’s fault.
Because this mistake causes small advertisers to pay for traffic they don’t need, the cost becomes too high for the sales the clicks bring in.
This is something I’ve been telling students and clients about for years.
Next, I want to show you something fresh: the true state of broad match keywords in 2020.
The Broad Match Experiment
If you’ve read any of my other articles on keyword match types, you probably know that I run a store that sells space posters.
Using that as an example, I’ve set up a campaign with a single ad group, a single broad match keyword: space posters, and no negative keywords.
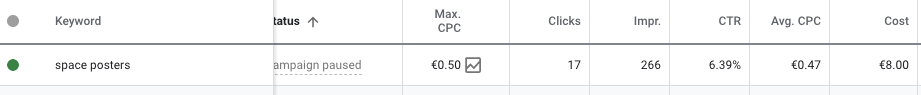
Here are the results:
- 17 clicks
- 6.39% CTR
- $0.52 CPC
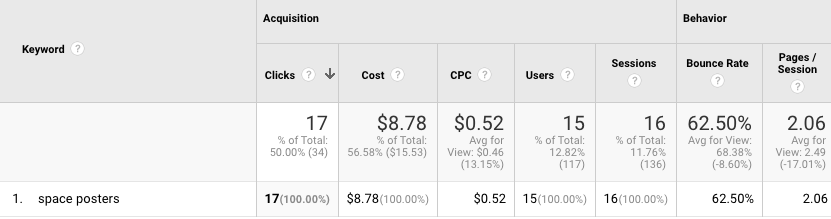
On the surface that looks ok. Plenty of clicks at a reasonable CPC. The traffic quality also isn’t too bad:
- bounce rate: 62.5%
- 2.06 pages / sessions
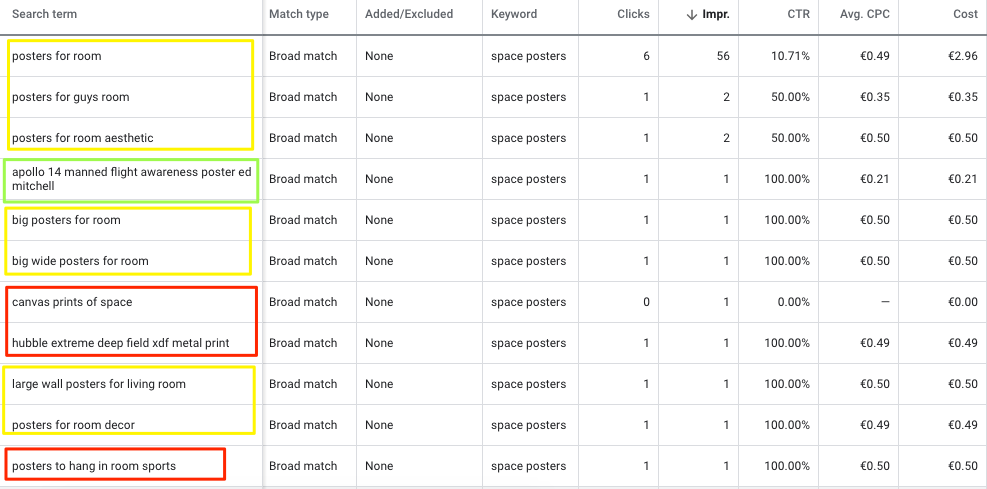
But if we take a look at the search queries that this keyword triggered, a different story emerges:
Of the 11 clicks in the screenshot, only one is actually space-related and relevant for my store (the green one).
The ones in yellow could be relevant but are very generic and it’s not clear from the search query what kind of poster they’d like to purchase. Since I only offer a very niche selection of posters, it’s unlikely that I can convert enough of these searches for it to be profitable.
The ones in red are irrelevant for my business and the products I sell. They have to do with the material (prints on canvas or metal), or about the topic “sports”.
The quality of these search queries is still acceptable, most queries talk about posters.
But the main problem is that it isn’t what the person setting up the campaign intended to happen. That shows itself in two ways:
1. Ads show up for very different search queries
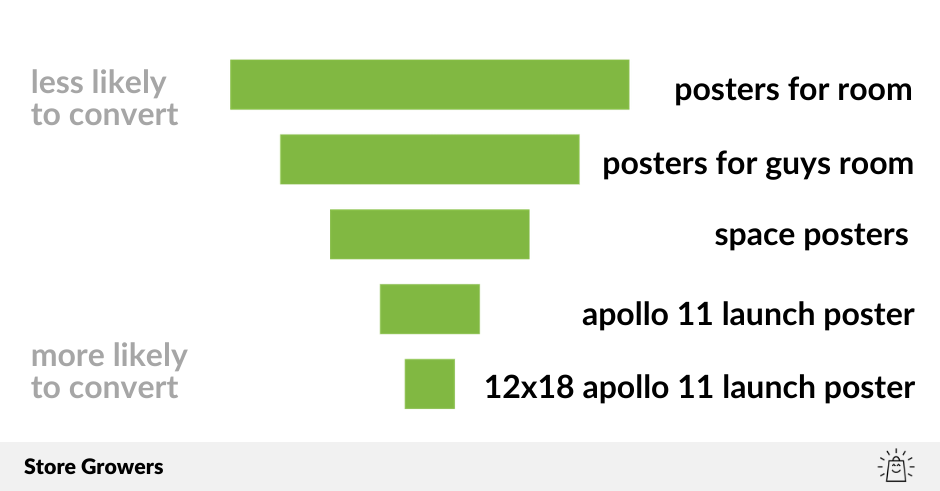
While the queries higher up the funnel could be interesting, you probably want to create a different campaign to target them. That way you can adapt set the appropriate CPC and create custom ad copy for the queries.
My approach with Search Ads is to start closest to the money and get those keywords profitable. Here that means running ads for the keywords in the bottom three slots of that funnel.
Only when I’m happy with those results, I can work my way further up the funnel and target some of those more generic ones.
2. The intended campaign structure breaks
Let’s say that instead of setting up only a single ad group, I do keyword research and find these other ad groups to be very valuable;
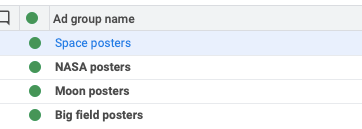
So besides the “Space posters” from above, I’ve added 3 other ad groups, every single one with its corresponding broad match keyword.
This complicates things because they can all show up for “posters for guys room” or “home decor posters”.
That violates my Golden Rule of Google Ads: a search query should only be able to show up in one place (campaign/ad group).
Because if it isn’t, how will you judge which keyword is actually performing well and which isn’t?
The way to control it is with an appropriate campaign structure, which broad match keywords kind of make impossible.
When Should I Use Broad Match?
For those of you that want to run a simple Search Ads campaign, skip the default match type, and build your ad groups using modified broad match is a good alternative.
If you’re interested, there are only a few situations when I still use broad match.
Situation 1 – Lazy keyword research
Doing keyword research is a time-consuming process.
You need to research good seed keywords, run them through the different tools, and then analyze all that information.
Running a broad match keyword research campaign allows you to get a lot of those done.
There are a couple of advantages to this approach:
- Real data: all tools, even Google’s own Keyword Planner, give you estimates of how many clicks a certain keyword will get. With your campaigns, you can see the actual numbers.
- Conversion data: in keyword research, you’ll only see the number of clicks. But if you’re running a real campaign, you might be able to spot a few keywords which result in actual sales.
- Instant negative keyword mining: since there will be a lot of irrelevant traffic, your negative keywords lists will be instantly built out.
The biggest downside, of course, is the cost that is involved. Each one of those clicks costs money. So if you’re on a shoestring budget, this is definitely not the way to go.
Situation 2 – Heavily build out negative keyword lists.
This section contains a pretty advanced approach. But since it’s one of the only times I use broad match, I wanted to show you how.
I hope all the above has made it clear why using broad match keywords as the default is a bad idea. It’s because you’ve got little control over where your ads appear.
Here are 3 ways to get back some control:
- Negative keywords: these allow you to filter out queries you don’t want OR that you’re already targeting with other campaigns
- Demographics: can you layer demographics information onto your broad campaign to focus on your target audiences
- Audiences: do you have any information about these people? Have they been to your site? On your email list? Part of an in-market audience?
Using a mix of the above can lead to a keyword research campaign that brings in interesting queries, without wasting too much money.
But as I said, you need to know what you’re doing with this campaign.
Situation 3 – Display campaigns
If you’re using Keywords as a targeting option for a Display campaign, you’ll need to use a broad match keyword.
That’s because its the only match type that’s supported 🙂
Negative broad match keywords
While regular broad match keywords are a poor choice, negative broad match keywords are used pretty often.
They are able to catch some variations of your negative keywords.
All that is required is to remove the default square brackets that Google Ads:
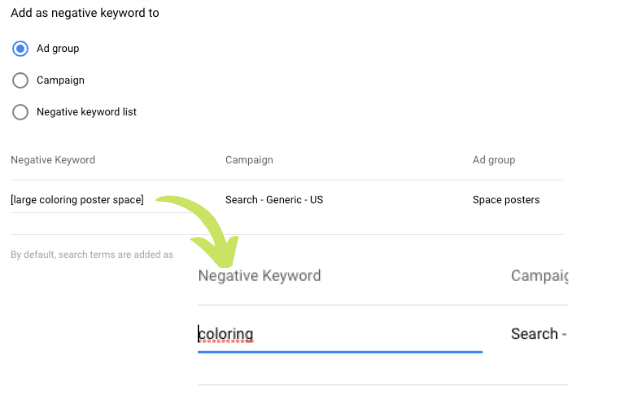
That will exclude any search query that involves the word coloring.
But a search like “color book with space images” would still come through. So to exclude those, you would need to add additional negative keywords (like “color”).
Broad Match vs Modified Broad Match
While the difference in syntax between the two is small, two quotation marks, the results are very different.
| Broad match | Modified broad match | |
| Syntax | None | + |
| Number of potential impressions | Very large | Large |
| Keyword research purposes | Very good | Good |
| Keyword + search query match | Very low | Good |
| Ad text + search query match | Very low | Reasonable |
| Landing page + search query match | Very low | Good |
Changes to Broad Match: Close Variants
Like the other match types, the broad match type has evolved over the years.
But since its very definition is to bring you a wide variety of search queries, the details of the exact definitions matter a lot less.
But for completeness sake, its close variants include misspellings, singular and plural forms, abbreviations and acronyms, stemmings, implied terms, synonyms and paraphrases, and variants of your keyword terms that have the same meaning.
👍👎The Verdict
Should you still use broad match keywords in 2020?
No.
Go for modified broad match keywords instead. You’ll get higher quality visitors and waste a lot less of your ad budget.